Successful case
科研解决方案

精准医学900K芯片,是为了加速精准医学研究,可提供高重现性结果,并能确保每个批次中的所有标记都能为我们所用的基因分型解决方案。
在精准医学筛查研究中,这款产品能够推动更深入的个体遗传多样性科学研究和理解。

1.基于 AxiomTM基因分型解决方案,广受生物信息样本库的青睐,可提供来自千人基因组计划的第III阶段以及 NHGRI-EBI GWAS 目录(2016年5月发布)中的全基因组imputation 骨架,为跨群体的疾病关联研究带来前沿的内容、广泛的覆盖面和高的准确度。
2.包含经过仔细选择、具有重要临床意义的致病性变异,包括那些与广泛群体中的实际遗传风险相关的致病性变异。按照 NHGRI-EB要求,覆盖通过GWAS识别出的癌症相关常见变异。
3.包含与免疫、移植相关的变异,包括可使用相应的AxiomTM HLA 分析软件分析的人白细胞抗原(HLA)标记,以及杀伤细胞免疫球蛋白样受体 (KIR),旨在加深移植相关研究中对排斥风险和原因的理解。
4.覆盖从 GWAS 和候选基因研究中选出的血液表型标记,这些内容包括与红细胞群、红细胞和血小板的形成调控,以及血液内平衡调控相关联的标记。
5.使用华盛顿大学和麻省理工学院-哈佛大学博德研究所 (Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard) 所提供的 SNP 作为指纹SNP。这些标记在多个主流基因分型平台上共享,用于样品追踪。

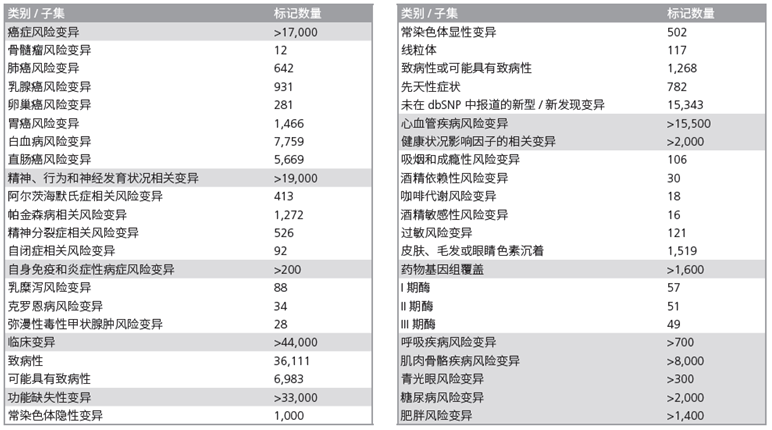
该芯片可以用于研究疾病和人类健康状况的变异。精准医学900K芯片包含数千个涉及人类疾病和健康状况的新型风险变异。该芯片包含选自 ClinVar 的致病性变异,包括与阿尔茨海默氏症相关的 ApoE 标记。到目前为止,还没有可提供此类标记的其他芯片产品。该芯片可以用于分析人体常见的癌症风险变异、精神健康和神经发育状况相关的变异、免疫相关的免疫以及心脑血管变异情况。
由于芯片是96制式的,需要满96样品才能起始实验,中玉金标记从收到样本到完成客户所需的分析需要一个月左右,如果客户需要定制化服务则可能需要更长的时间。
1. Ma J., et al. Association analysis of the cubilin (CUBN) and megalin (LRP2) genes with ESRD in African Americans. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 11(6):1034—1043 (2016).
2. Davies G., et al. Genome-wide association study of cognitive functions and educational attainment in UK Biobank (N=112,151). Molecular Psychiatry 21:758–767 (2016).
3. Day F. R., et al. Physical and neurobehavioral determinants of reproductive onset and success. Nature Genetics 48:617–623 (2016).
4. Li Y. R., et al. Concept and design of a genome-wide association genotyping array tailored for transplantation-specific studies. Genome Medicine 7:90 (2015).
5. Lambert J. C., et al. Meta-analysis of 74,046 individuals identifies 11 new susceptibility loci for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature Genetics 45(12):1452–1458 (2013).
6 Joshi P. K., et al. Variants near CHRNA3/5 and APOE have age- and sex-related effects on human lifespan. Nature Communications 7:11174 (2016).
7. Al-Tassan N. A., et al. A new GWAS and meta-analysis with 1000 Genomes imputation identifies novel risk variants for colorectal cancer. Scientific Reports 5:10442 (2015).
8. Hoffmann T. J., et al. Imputation of the rare HOXB13 G84E mutation and cancer risk in a large population-based cohort. PLoS Genetics 11(1):e1004930 (2015).
9. Permuth J. B., et al. Exome genotyping arrays to identify rare and low frequency variants associated with epithelial ovarian cancer risk. Human Molecular Genetics doi:10.1093/hmg/ddw196 (2016).
10. Kachuri L., et al. Fine mapping of chromosome 5p15.33 based on a targeted deep sequencing and high density genotyping identifies novel lung cancer susceptibility loci. Carcinogenesis 37(1):96–105 (2016).
11. Gale C. R., et al. Pleiotropy between neuroticism and physical and mental health: findings from 108,038 men and women in UK Biobank. Translational Psychiatry 6:e791 (2016).
12. Smith D. J., et al. Genome-wide analysis of over 106,000 individuals identifies 9 neuroticism-associated loci. Molecular Psychiatry 21(6):749–757 (2016).
13. Han F., et al. Genome wide analysis of narcolepsy in China implicates novel immune loci and reveals changes in association prior to versus after the 2009 H1N1 influenza pandemic. PLoS Genetics 9(10):e1003880 (2013).